Table of Contents
ToggleSource of FKM
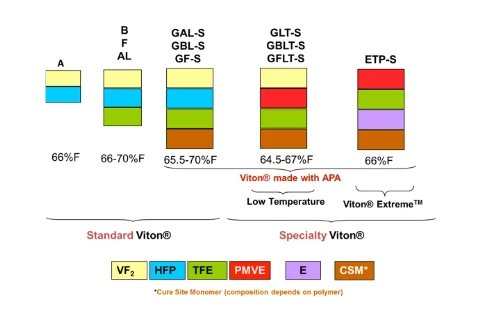
In 1957, DuPont developed the first FKM material to meet the demanding sealing requirements of the aerospace industry. Later, in 1959, a ternary copolymer of tetrafluoroethylene (TFE) was introduced, offering improved thermal stability and solvent resistance. Currently, the most common global FKM brands include Chemours’ Viton®, Solvay’s Tecnoflon®, 3M’s Dyneon™, and Daikin’s DAI-EL™.
FKM Temperature Range and Performance
The operating temperature range of FKM (Viton®) typically includes:
Continuous working temperature: -20°C to +200°C
Short-term temperature resistance: up to +260°C
FKM is known for its excellent high temperature resistance (-20°C to 260°C) and strong anti-aging and chemical corrosion resistance. For example, it resists oils, acids, and solvents, making it compatible with nearly all lubricants, fuel oils, and gasoline. Moreover, it does not easily harden in oils containing extreme pressure additives, which is why it is the top choice for high-end seals. However, it has some drawbacks, such as high permanent compression deformation, poor high-temperature wear resistance, and limited cold resistance. That said, specially modified types (e.g., low-temperature FKM) can withstand harsh environments as low as -40°C, though at a higher cost.
Application Areas of FKM
Key industry field applications include:
- Hydraulic systems seals in loading/unloading trucks, including large-scale vehicles
- Semiconductor equipment (seals for etching and deposition processes)
- Defense, military, aerospace, automotive, and petrochemical sealing components
- High-corrosion-resistant seals for chemical pipelines and valves